Activate Microsoft Office 2010 Volume for FREE
Step 1 : You visit bit.ly/Office2010
Step 2 : You copy the code above into a new text document

Step 3 : You save it as a batch file , name “Office2010.cmd”

Step 3 : You save it as a batch file , name “Office2010.cmd”
Note : IF you use windows 10, you save it as .bat (named “Office2010.bat”)

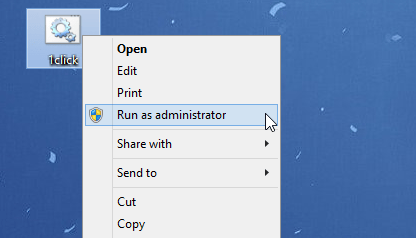
Step 4 : You run the batch file as administrator
Done! You Office has been activated successfully. Please check activation status again.
You can watch this video to know How to Activate Microsoft Office 2010 without Product Key 2019
Call wait/hold/forwarding Activate & Deactivate ideas of NTC

- Here are some method of Call wait/hold/forwarding Activate & Deactivate ideas of NTC.
- What is Call Wait feature?
Call waiting feature informs customer about incoming call even if the customer is busy talking with another customer.
- How to activate/deactivate Call Wait feature.
Option to activate deactivate call wait feature is normally present inside "Call Setting" menu of the phone. Or you can activate dialing *43# .Deactivate Using #43#. Check Call waiting status using code *#43#.
- Need to pay for Call Wait?
No need to pay. It is free for Nepal Telecom subscriber.
- What is Call Hold feature?
Call hold feature allows customer to place an active call on hold and initiate another call or answer an incoming call.
- How to Activate/De-activateCall hold feature?
Nepal Telecom have already provisioned this feature for all its valued customer.
- Need to pay for Call hold?
No need to pay. It is free for all Nepal Telecom subscriber.
- What is Call forwarding?
Call forwarding allows you to forward your incoming calls to another phone number.
- Types of Call Forwarding?
a. Unconditional Call Forwarding ( dial **21*Number# to activate )
Forwards all of your incoming call to another phone number.
b. Call Forwarding when busy (Dial **67* Number# to activate)
Forwards an incoming call when you are busy with another call.
c. Call forwarding when no reply (**61*Number# to activate)
Forwards the call when you did not answer an incoming call.
d. Call forwarding when not reachable (**62*Number# to activate)
Forwards the call when your phone is out of network coverage or phone is switched off.
- How to Activate/De-activate Call Forwarding?
Option to activate/deactivate above mentioned types of call forwarding is normally present inside "Call Setting" menu of the phone.or
a. Unconditional Call Forwarding ( dial **21*Number# to activate,##21# to deactivate)
b. Call Forwarding when busy(Dial **67* Number# to activate,##67 # to deactivate)
c. Call forwarding when no reply( dial **61*Number# to activate,##61 # to deactivate)
d. Call forwarding when not reachable( dial **62*Number# to activate, ##62# to deactivate)
- Need to pay for Call forwarding feature?
If "A-number" is making call to "B-number" and "B-number" forwards call to "C-number" then "A-number" pays as if it is calling "B-number" and "B-number" needs to pay as if it is calling "C-number".
- Any limitation to Call forwarding feature?
Calls can only be forwared to NT Network (PSTN/GSM/CDMA).
Call forwarding when busy and call Wait feature cannot be simultaneously active.
If you have NTPro , then you already have set call forwarding when not reachable to NTpro platform, if you again set unreachable forwarding to another number, your NTpro incoming will not work.
source: NTC

Call waiting feature informs customer about incoming call even if the customer is busy talking with another customer.
Option to activate deactivate call wait feature is normally present inside "Call Setting" menu of the phone. Or you can activate dialing *43# .Deactivate Using #43#. Check Call waiting status using code *#43#.
No need to pay. It is free for Nepal Telecom subscriber.
Call hold feature allows customer to place an active call on hold and initiate another call or answer an incoming call.
Nepal Telecom have already provisioned this feature for all its valued customer.
No need to pay. It is free for all Nepal Telecom subscriber.
Call forwarding allows you to forward your incoming calls to another phone number.
a. Unconditional Call Forwarding ( dial **21*Number# to activate )
Forwards all of your incoming call to another phone number.
b. Call Forwarding when busy (Dial **67* Number# to activate)
Forwards an incoming call when you are busy with another call.
c. Call forwarding when no reply (**61*Number# to activate)
Forwards the call when you did not answer an incoming call.
d. Call forwarding when not reachable (**62*Number# to activate)
Forwards the call when your phone is out of network coverage or phone is switched off.
Option to activate/deactivate above mentioned types of call forwarding is normally present inside "Call Setting" menu of the phone.or
a. Unconditional Call Forwarding ( dial **21*Number# to activate,##21# to deactivate)
b. Call Forwarding when busy(Dial **67* Number# to activate,##67 # to deactivate)
c. Call forwarding when no reply( dial **61*Number# to activate,##61 # to deactivate)
d. Call forwarding when not reachable( dial **62*Number# to activate, ##62# to deactivate)
If "A-number" is making call to "B-number" and "B-number" forwards call to "C-number" then "A-number" pays as if it is calling "B-number" and "B-number" needs to pay as if it is calling "C-number".
Calls can only be forwared to NT Network (PSTN/GSM/CDMA).
Call forwarding when busy and call Wait feature cannot be simultaneously active.
If you have NTPro , then you already have set call forwarding when not reachable to NTpro platform, if you again set unreachable forwarding to another number, your NTpro incoming will not work.
HTTP Error Codes and their meaning
Following are the HTTP Error Codes. If you can interpret the correct meaning of the http error code, you can decide the places to look at for resolving this issue.
These status codes indicate a provisional response. The client should be prepared to receive one or more 1xx responses before receiving a regular response.
* 100 - Continue.
* 101 - Switching protocols.
* 101 - Switching protocols.
2xx - Success
This class of status codes indicates that the server successfully accepted the client request.
* 200 - OK. The client request has succeeded.
* 201 - Created.
* 202 - Accepted.
* 203 - Non-authoritative information.
* 204 - No content.
* 205 - Reset content.
* 206 - Partial content.
* 207 - Multi-Status (WebDay).
3xx - Redirection
* 201 - Created.
* 202 - Accepted.
* 203 - Non-authoritative information.
* 204 - No content.
* 205 - Reset content.
* 206 - Partial content.
* 207 - Multi-Status (WebDay).
3xx - Redirection
The client browser must take more action to fulfill the request. For example, the browser may have to request a different page on the server or repeat the request by using a proxy server.
* 301 - Moved Permanently
* 302 - Object moved.
* 304 - Not modified.
* 307 - Temporary redirect.
4xx - Client Error
* 302 - Object moved.
* 304 - Not modified.
* 307 - Temporary redirect.
4xx - Client Error
An error occurs, and the client appears to be at fault. For example, the client may request a page that does not exist, or the client may not provide valid authentication information.
* 400 - Bad request.
* 401 - Access denied. IIS defines several different 401 errors that indicate a more specific cause of the error. These specific error codes are displayed in the browser but are not displayed in the IIS log:
o 401.1 - Logon failed.
o 401.2 - Logon failed due to server configuration.
o 401.3 - Unauthorized due to ACL on resource.
o 401.4 - Authorization failed by filter.
o 401.5 - Authorization failed by ISAPI/CGI application.
o 401.7 – Access denied by URL authorization policy on the Web server. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
* 401 - Access denied. IIS defines several different 401 errors that indicate a more specific cause of the error. These specific error codes are displayed in the browser but are not displayed in the IIS log:
o 401.1 - Logon failed.
o 401.2 - Logon failed due to server configuration.
o 401.3 - Unauthorized due to ACL on resource.
o 401.4 - Authorization failed by filter.
o 401.5 - Authorization failed by ISAPI/CGI application.
o 401.7 – Access denied by URL authorization policy on the Web server. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
* 403 - Forbidden. IIS defines several different 403 errors that indicate a more specific cause of the error:
o 403.1 - Execute access forbidden.
o 403.2 - Read access forbidden.
o 403.3 - Write access forbidden.
o 403.4 - SSL required.
o 403.5 - SSL 128 required.
o 403.6 - IP address rejected.
o 403.7 - Client certificate required.
o 403.8 - Site access denied.
o 403.9 - Too many users.
o 403.10 - Invalid configuration.
o 403.11 - Password change.
o 403.12 - Mapper denied access.
o 403.13 - Client certificate revoked.
o 403.14 - Directory listing denied.
o 403.15 - Client Access Licenses exceeded.
o 403.16 - Client certificate is untrusted or invalid.
o 403.17 - Client certificate has expired or is not yet valid.
o 403.18 - Cannot execute requested URL in the current application pool. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
o 403.19 - Cannot execute CGIs for the client in this application pool. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
o 403.20 - Passport logon failed. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
o 403.2 - Read access forbidden.
o 403.3 - Write access forbidden.
o 403.4 - SSL required.
o 403.5 - SSL 128 required.
o 403.6 - IP address rejected.
o 403.7 - Client certificate required.
o 403.8 - Site access denied.
o 403.9 - Too many users.
o 403.10 - Invalid configuration.
o 403.11 - Password change.
o 403.12 - Mapper denied access.
o 403.13 - Client certificate revoked.
o 403.14 - Directory listing denied.
o 403.15 - Client Access Licenses exceeded.
o 403.16 - Client certificate is untrusted or invalid.
o 403.17 - Client certificate has expired or is not yet valid.
o 403.18 - Cannot execute requested URL in the current application pool. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
o 403.19 - Cannot execute CGIs for the client in this application pool. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
o 403.20 - Passport logon failed. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
* 404 - Not found.
o 404.0 - (None) – File or directory not found.
o 404.1 - Web site not accessible on the requested port.
o 404.2 - Web service extension lockdown policy prevents this request.
o 404.3 - MIME map policy prevents this request.
* 405 - HTTP verb used to access this page is not allowed (method not allowed.)
* 406 - Client browser does not accept the MIME type of the requested page.
* 407 - Proxy authentication required.
* 412 - Precondition failed.
* 413 – Request entity too large.
* 414 - Request-URI too long.
* 415 – Unsupported media type.
* 416 – Requested range not satisfiable.
* 417 – Execution failed.
* 423 – Locked error.
o 404.1 - Web site not accessible on the requested port.
o 404.2 - Web service extension lockdown policy prevents this request.
o 404.3 - MIME map policy prevents this request.
* 405 - HTTP verb used to access this page is not allowed (method not allowed.)
* 406 - Client browser does not accept the MIME type of the requested page.
* 407 - Proxy authentication required.
* 412 - Precondition failed.
* 413 – Request entity too large.
* 414 - Request-URI too long.
* 415 – Unsupported media type.
* 416 – Requested range not satisfiable.
* 417 – Execution failed.
* 423 – Locked error.
5xx - Server Error
The server cannot complete the request because it encounters an error.
* 500 - Internal server error.
o 500.12 - Application is busy restarting on the Web server.
o 500.13 - Web server is too busy.
o 500.15 - Direct requests for Global.asa are not allowed.
o 500.16 – UNC authorization credentials incorrect. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
o 500.18 – URL authorization store cannot be opened. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
o 500.19 - Data for this file is configured improperly in the metabase.
o 500.100 - Internal ASP error.
o 500.13 - Web server is too busy.
o 500.15 - Direct requests for Global.asa are not allowed.
o 500.16 – UNC authorization credentials incorrect. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
o 500.18 – URL authorization store cannot be opened. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
o 500.19 - Data for this file is configured improperly in the metabase.
o 500.100 - Internal ASP error.
* 501 - Header values specify a configuration that is not implemented.
* 502 - Web server received an invalid response while acting as a gateway or proxy.
o 502.1 - CGI application timeout.
o 502.2 - Error in CGI application.
* 503 - Service unavailable. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
* 504 - Gateway timeout.
* 505 - HTTP version not supported.
* 502 - Web server received an invalid response while acting as a gateway or proxy.
o 502.1 - CGI application timeout.
o 502.2 - Error in CGI application.
* 503 - Service unavailable. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
* 504 - Gateway timeout.
* 505 - HTTP version not supported.
पासवर्ड ह्याकिङ
प्रविधिको प्रयोग र
पहुँच बढेसँगै ह्याकिङको विषयमा पनि धेरै चर्चा भईरहेको पाइन्छ । ह्याकरले
पासवर्ड ह्याक गर्न अपनाउने तरिकाबारेमा धेरै कमै मानिसहरुलाई थाहा हुन सक्छ । तर तपाईले
ह्याकिङबारेमा थोरै जानकारी लिनुभयो भने यो समस्याबाट सजिलै बच्न
सक्नुहुन्छ । ह्याकरहरुले कसरी पासवर्ड ह्याक गर्न सक्छन, केही प्रचलित तरिकाहरु प्रस्तुत गर्न खोजेको छु ।
१. डिक्सनरी ह्याक
यो एक यस्तो उपाय हो
जुन ह्याकरहरुले सबैभन्दा धेरै प्रयोग गर्ने गर्दछन् । यसमा ह्याकरले पासवर्ड
ह्याक नहुन्जेल डिक्शनरीको सहायता लिएर धेरै शब्दहरु प्रयोग गर्छन् । यो उपायबाट ५४
प्रतिशत पासवर्ड क्र्याक गरि ह्याक गरिन्छ ।
यसबाट बच्नलाई बलियो
पासवर्ड राख्नुस जसले तपाईको लगइनमा ह्याकरले सजिलै आक्रमण गर्न सक्दैनन् ।
२. ब्रुट फोर्स अट्याक्स
ह्याकरहरुसंग लाखौ, करोडौ सम्भावित पासवर्डहरुको List हुन्छ । जबसम्म उनीहरुले तपाईको पासवर्ड थाहा
पाउँदैनन् तबसम्म यो उपाय लगाइरहन्छन् । ह्याकर्सले तपाईँको पासवर्ड थाहा पाउन अनुमानको भरमा पनि
पासवर्ड खोजिरहेका हुन्छन् । १२३४५६ अहिलेसम्म प्राय सबैभन्दा साझा
पासवर्ड मानिन्छ । जसलाई धेरै प्रयोगकर्ताले पासवर्डको रुपमा प्रयोग गर्ने
गर्दछन् । यसैको साथमा पासवर्ड,
युजरनेम,
बर्थडे,
बर्थ प्लेस, पेट्स नेम आदिको
प्रयोग गरेर समेत उनीहरु सजिलै तपाईँको एकाउन्ट ह्याक गर्न सक्छन् ।
यसबाट बच्न आफ्नो नाम
र मेल आइडीको युजर नेम, बर्थ डेट लगातको पासवर्ड प्रयोग नगर्नुस् ।
३. फिसिङ अट्याक्क
फिसिङ अट्याक्क एक
प्रकारको पासवर्ड अट्याक्क गर्ने सजिलो माध्यम हो । फिसिङ भन्नाले नक्कली
वेबसाइटमा आफ्नो एकाउन्ट खोलेर फस्नु भन्ने बुझिन्छ । जस्तै फेसबुक जस्तै नक्कली वेवसाईट बनायर तपाईको असली फेसबुकको पासवर्ड थाहा पाउनु । यसमा तपाईले आफनो लग इन गर्ने बित्तिकै तपाईको सम्पूर्ण आइडी र
पासवर्डहरु ह्याकरले ह्याक गर्न सक्छन् ।
यसबाट बच्न कुनै पनि
वेबसाइटमा लगइन गर्नुभन्दा पहिले उसको सुरक्षामा चेक गर्नुस् । URL मा लगको संकेत भएमा उक्त साइट पुरै सुरक्षित भएको मानिन्छ । URL मा आफैले टाइप गर्ने बानी बसालौ, कुनैपनि link वा Hyperlink को प्रयोग राम्रो संग बुझेरमात्र गर्दा राम्रो हुन्छ । कुनैपनि फेक/नक्कली वेवसाईटमा लगइन नगर्नु धेरै बुद्धिमानी हुन्छ ।
४. की लगर अट्याक
यो पनि पासवर्ड हयाक
गर्ने फिसिङ अट्याक्कको दोस्रो तरिका हो । यसमा इमेल मार्फत आउने अट्याचमेन्टसँग
सम्बन्धित हुन्छ । अपरिचित व्यक्तिबाट इमेलमा आएको अट्याचमेन्ट डाउनलोड गर्ने बित्तिकै हामीले थाहै नपाईकन हाम्रो सम्पूर्ण जानकारी ह्याकरको नियन्त्रणमा
पुग्छ । त्यसपछि हाम्रो ब्राउजर क्र्यास हुने,
राम्ररी पेज नखुल्ने र खोले पनि ढिला खुल्ने लगायतका समस्या देखा पर्छ । त्यसपछि हामीले चलाएको
सबै कुराहरु ह्याकरको नियन्त्रणमा पुग्छ । जसबाट हाम्रो पासवर्ड ह्याक हुन
जान्छ।
यसबाट बच्न हामीले
अपरिचित व्यक्तिबाट इमेलमा आएको अट्याचमेन्ट डाउनलोड गर्नु हुदैन ।
५. रेन्बो टेबल
रेन्बो टेबल एक यस्तो
टेबल हो जसमा धेरै नम्बरहरुमा इनक्रिप्टेड पासवर्ड अर्थात हाम्रो पासवर्डको नाम, नम्बर, बर्थडे आदि लगायतको कुराहरु समावेश गरिएको हुन्छ । जुन हामीलाई यी कुराहरु टेबल मार्फत प्रयोग
गर्न बाध्य बनाउँछ । प्रतियोगीताको नाममा होस वा गेमको नाममा हामीलाई फसाँउदै
जान्छन । यो उपायका लागि ह्याकरहरु कम्प्युटरमा पुरै दक्ष भइसकेका हुन्छन । जसबाट
ह्याकरले रेन्बो टेबललाई किनेर पासवर्ड ह्याक गर्छन् ।
यसबाट बच्न कुनैपनि गेम वा प्रतियोगितामा सहभागी हुनु पूर्व त्यसको बारेमा राम्रो संग बुझेर सहभागी हुनु उचित हुन्छ ।
६. स्पाइडरिङ
ह्याकरहरु धेरै जसो
कर्पोरेट सिष्टमहरुलाई ह्याक गर्न निकै सक्रिय रहेका हुन्छन् । उसले
कर्पोरेटको विजनेससँग सम्बन्धित शब्दहरुको प्रयोग गर्छन् । उनीहरुले
पासवर्ड ह्याक गर्न कम्पनीको वेबसाइट,
बिक्रीका लागि राखिएका सामग्री, पर्चाहरुमा अनुसन्धान गरिरहेका हुन्छन् । यसलाई नै टेक्निकल
भाषामा स्पाइडरिङ भन्ने गरिन्छ ।
यसबाट बच्न कम्पनीसँग
मिल्ने इमेल अथवा कम्पनीको नाममा पासवर्ड राखिएको हुन्छ । त्यसलाई तत्कालै परिवर्तन
गर्नुस्।Types of Cybercrime
An attack to commit a Cyber Crime can be called as a Cyber
Attack! When it comes to the Internet, you are sure to acquire some
malware, if you visit malicious websites without proper protection. At the
minimum, you need an antivirus and a firewall. You also need to stay and steer
clear of different types of cybercriminals trying to make money at your cost.
It is important to note that a computer, Internet or
computer technology has to be involved, and when the use of any of the
following techniques or activities is made to carry out a crime or illegal
activity – only then can it be classified as a Cybercrime.
Identity theft
Identity theft is a crime in which an imposter obtains key
pieces of personal information, such as Social Security or driver's license
numbers, in order to impersonate someone else. The information can be used to
obtain credit, merchandise, and services in the name of the victim, or to
provide the thief with false credentials. In addition to running up debt, an
imposter might provide false identification to police, creating a criminal
record or leaving outstanding arrest warrants for the person whose identity has
been stolen.
Ransomware
This is one of the detestable malware-based attacks.
Ransomware enters your computer network and encrypts your files using
public-key encryption, and unlike other malware this encryption key remains on
the hacker’s server. Attacked users are then asked to pay huge ransoms to
receive this private key.
DDoS attacks
DDoS attacks are used to make an online service unavailable
and bring it down, by bombarding or overwhelming it with traffic from
multiple locations and sources. Large networks of infected computers, called
Botnets are developed by planting malware on the victim computers. The idea is
normally to draw attention to the DDOS attack, and allow the hacker to hack
into a system. Extortion and blackmail could be the other motivations.
Botnets
Botnets are networks of
compromised computers, controlled by remote attackers in order to perform such
illicit tasks as sending spam or attacking other computers. Computer Bots
can also be used act like malware and carry out malicious tasks. Then can be
used to assemble a network of computers and then compromise them.
Spam and Phishing
Spamming and phishing are two very common
forms of cybercrimes. There is not much you can do to control them. Spam is
basically unwanted emails and messages. They use Spambots. Phishing is a method where cyber
criminals offer bait so that you take it and give out the information they
want. The bait can be in form of a business proposal, announcement of a lottery
to which you never subscribed, and anything that promises you money for nothing
or a small favor. There are online loans companies too; making claims that you
can get insecure loans irrespective of your location. Doing business with such
claims, you are sure to suffer both financially and mentally. Phishing
has its variants too – notably among them are Tabnabbing, Tabjacking. And Vishing and Smishing. Such spamming
and phishing attempts are mostly emails sent by random people whom you did not
ever hear of. You should stay away from any such offers especially when you
feel that the offer is too good. The US Cybercrime Center says – do not
get into any kind of agreements that promise something too good to be true. In
most cases, they are fake offers aiming to get your information and to get your
money directly or indirectly.
Social Engineering
Social engineering is a method where the cyber criminals
make a direct contact with you using emails or phones mostly the latter. They try to gain your
confidence and once they succeed at it, they get the information they need.
This information can be about you, your money, your company where you work or
anything that can be of interest to the cyber criminals. It is easy to find out
basic information about people from the Internet. Using this information as the
base, the cyber criminals try to befriend you and once they succeed, they will
disappear, leaving you prone to different financial injuries directly and
indirectly. They can sell the information obtained by you or use it to secure
things like loans in your name. The latter case is of Identity theft. You
should be very careful when dealing with strangers – both on phone and on the
Internet.
Malvertising
Malvertising is a method whereby users download malicious
code by simply clicking at some advertisement on any website that is infected.
In most cases, the websites are innocent. It is the cyber criminals who insert
malicious advertisements on the websites without the knowledge of the latter.
It is the work of advert companies to check out if an advertisement is
malicious but given the number of advertisements they have to deal with, the
malverts easily pass off as genuine ads. In other cases, the cyber criminals
show clean ads for a period of time and then replace it with malverts so that
the websites and advertisements do not suspect. They display the malverts for a
while and remove it from the site after meeting their targets. All this is so
fast that the website does not even know they were used as a tool for
cybercrime. Malvertising is one of the fastest, increasing types of cybercrime.
PUPs
PUPs, commonly known as Potentially Unwanted Programs are
less harmful but more annoying malware. It installs unwanted software in your
system including search agents and toolbars. They include spyware, adware, as
well as dialers. Bitcoin miner was one of the most commonly noticed PUPs in
2013.
Drive-By-Downloads
Drive By Downloads too, come close to malvertising. You
visit a website and it triggers a download of malicious code to your computer.
These computers are then used to aggregate data and to manipulate other
computers as well. The websites may or may not know that they have been
compromised. Mostly, the cyber criminals use vulnerable software such as Java
and Adobe Flash and Microsoft Silverlight to inject malicious codes as soon as
a browser visits the infected website. The user does not even know that there is
a download in progress.
Remote Administration Tools
Remote Administration Tools are used to carry out illegal
activities. It can be used to control the computer using shell commands, steal
files/data, and send location of the computer to a remote controlling device
and more.
Exploit Kits
Vulnerability means some problem in the coding of software
that enables cyber criminals to gain control of your computer. There are ready
to use tools (exploit kits) in the Internet market which people can buy and use
it against you. These exploit kits are upgraded just like normal software. Only
difference is these are illegal. They are available mostly in hacking forums as
well as on the Darknet.
Scams
Notable among Internet scams are, scams which misuse the
Microsoft name and other general tech support scams. Scamsters phone computer
users randomly and offer to fix their computer for a fee. Every single day,
scores of innocent people are trapped by scam artists into Online Tech Support
Scams and forced to shell out hundreds of dollars for non-existent computer
problems.
Manual install Apache, PHP and MySQL
Step 1: Install MySQL
- Install the MySQL database server on your PC. We will do this using the 'MSI' one-click installer for Windows. Go to http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/ and download the 'MySQL Installer for Windows'. At the time of writing this was from a very obvious graphic at the top of the screen (which I missed the first time).
- Run the installation. Click...
- Install MySQL products
- Accept the license
- Allow the version check (optional)
- At 'Choose a Setup Type' accept the "Developer Default" and click Next
- A number of downloads of required software may be identified. Click Execute and follow onscreen instructions to install them.
- At 'Installation progress' screen, hit Execute - the MySQL software will be installed
- At 'Configuration overview' hit Next to go to the basic configuration screen.
- Accept all the defaults on the 'MySQL Server Configuration' and hit Next.
- On the password screen, supply a password for the 'root' (main administrator) user. Make sure it's one you won't forget. You can also create a 'User' account just for Moodle with more restricted access if you like. This would be good practice on a public server but just using the 'root' user will suffice for testing.
- On the Service details page, accept the defaults and hit Next and then Next a couple more times for the configuration progress.
- Click Finish. Job done.
- MySQL Workbench will open. Under Server Administration (right hand column, double click 'Local MySQL56' (or whatever you called it). A box should pop up asking for the root password. Enter the password you supplied
- The server management screen should appear. You don't have to worry too much about this. It just shows the install is working.
- Install the Apache web server on your PC. Go to http://www.apachelounge.com/download/. Scroll down the page until you find the download for the 'Apache 2.4 win32 binaries' and download. You need to be careful that the module dll in PHP matches the version of Apache you install. Apache won't load otherwise.
- Unzip the file into C:\. You should end up with a directory 'Apache24' (or whatever the latest version is).
- Find Start > All programs > Accessories > Command Prompt...... BUT, right click, and select 'Run as administrator'.
- Enter the following commands
cd \Apache24\bin httpd -k install httpd -k start...you may well get a warning about the server name. Don't worry about it. Don't close this window, you will need it again in a minute.
- To test it worked type 'http://localhost' into your browser. You should get a screen up to the effect that Apache is installed and working.
Step 3: Install PHP
- Now install the PHP scripting language on your PC. Go to http://www.php.net/download. In the current stable release section click on link for Windows 5.x.x binaries and source. Scroll down to the newest 'Zip' for VC11 x86 Thread Safe (non thread safe doesn't have the Apache dll) PHP (again, the newest versions of PHP didn't have this but it shouldn't matter) and download. *Don't* be tempted to use the Microsoft Installer version; it won't work.
- Open the zip file and extract to C:\PHP\
Step 4: Configure Apache and PHP
You now need to edit Apache's httpd.conf file. In the file explorer navigate to C:\Apache24\conf\httpd.conf. Open it in Notepad . At the end of this file (or wherever you like if you want to be more organised) add the following lines:LoadModule php5_module "C:/PHP/php5apache2_4.dll" AddHandler application/x-httpd-php .php PHPIniDir C:/PHPThe version of the module file matters (2_4 in this case). It MUST match the Apache version installed.
In the same file. Search for the line starting DirectoryIndex. Change it as follows
DirectoryIndex index.php index.htmlNow, navigate to C:\PHP, and copy php.ini-development to php.ini. Edit this file, find the following lines and modify them as follows (all should exist already):
memory_limit = 256M post_max_size = 128M upload_max_filesize = 128MYou need to specify the extensions required for Moodle. Find the 'Dynamic Extensions' section and change the following lines (uncomment and add the correct path):
extension=c:/php/ext/php_curl.dll extension=c:/php/ext/php_gd2.dll extension=c:/php/ext/php_intl.dll extension=c:/php/ext/php_mbstring.dll extension=c:/php/ext/php_mysqli.dll extension=c:/php/ext/php_openssl.dll extension=c:/php/ext/php_soap.dll extension=c:/php/ext/php_xmlrpc.dll(these are a minimum. You may need others - e.g. LDAP - for specific functions) ...and save.
Back in the 'cmd' window for Apache, you need to restart it to load your changes...
httpd -k restart
Step 5: Test your install
Navigate to C:\Apache24\htdocs and create a file called 'test.php'. I had to change a file explorer setting to create .php files - Organise > Folder and search options > View and then untick 'Hide extensions for known file types'.In this file enter the single line...
And then, in your browser, navigate to http://localhost/test.php. You should see a screen with masses of information and the PHP logo at the top. Check a few lines down for 'Loaded Configuration File' and make sure it says c:\php\php.ini. That's PHP and Apache all working :)
Subscribe to:
Comments
(
Atom
)